Houston is a city that never stops building. Its skyline is constantly shifting, a physical reflection of its relentless economic growth. Yet, where this growth once relied solely on hammers, concrete, and human hands in hard hats, a new, unexpected player is now entering the construction site: the robot.
The engineering heart of Texas couldn’t stand apart from the global wave of automation. With rising labor costs and a critical need to boost safety, local companies have started heavily integrating artificial intelligence and sophisticated robotics. This isn’t just swapping a person for a machine; it’s a fundamental change to the rules of the game. At i-houston.com, we’ll explore how these “silicon builders” are already transforming the process of erecting skyscrapers, roads, and residential complexes, making Houston not just a city of the future, but a city built by the future.
From Hard Hats to Code
Houston, the fourth-largest city in the U.S., constructs thousands of square meters of residential and office space annually. According to the American Institute of Architects, the industry is grappling with a severe labor shortage—up to 500,000 vacancies nationwide. In response, local startups are weaving AI into daily operations. Instead of manually chalking lines onto concrete, autonomous devices print blueprints directly onto surfaces, cutting layout time in half. This isn’t science fiction: real-world examples from the Mesquite Government Center show how these tools are reducing errors by 75%. The rise of “construction bots” here is not a luxury, but a growth imperative.
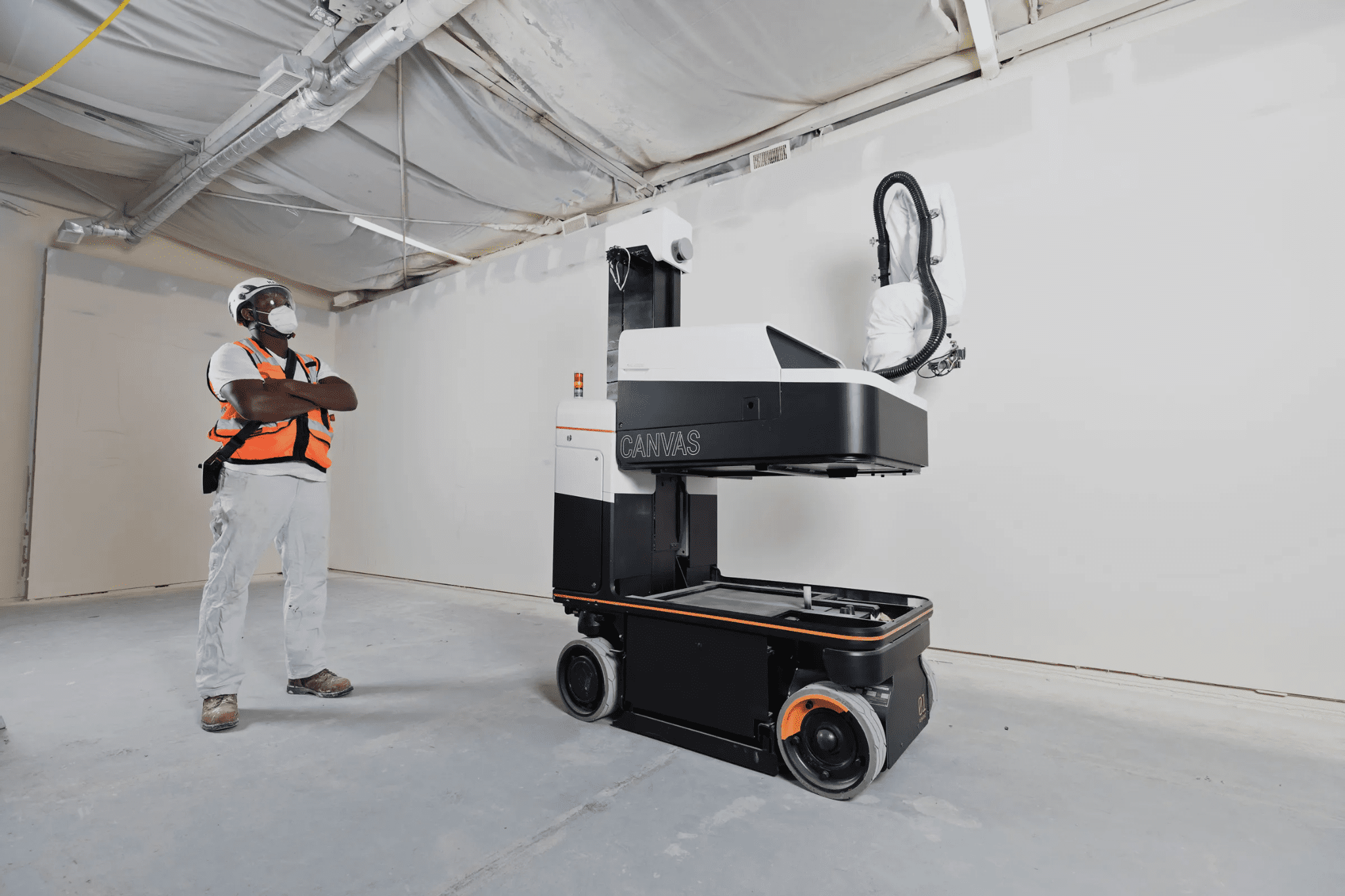

Texas-Sized Innovation
The story starts with a dynamic duo: engineer Derrick Morse, who managed commercial projects for years, and roboticist Logan Farrell, a former NASA employee. In 2018, they co-founded Rugged Robotics in the city’s industrial district. The founders say the idea originated on real sites where manual element placement took weeks and sparked conflicts between crews. Today, the firm, according to PitchBook, has raised $11.9 million in investment from venture funds like Suffolk Technologies. This is a typical Houston success story: marrying the city’s energy heritage with space-age technology to make the industry more resilient to crises.
Key Players in the Arena
Houston has always been a magnet for engineering talent. But now, the city is attracting not just oil explorers, but automation pioneers. This is forging a powerful ecosystem for construction robotics.
Several companies are leading the charge in this new sector. Rugged Robotics focuses on commercial projects, specializing in automated site layout solutions. This dramatically increases the accuracy and speed of preparatory work. Another major player is DynaRobot, established back in the 2000s. It focuses on integrating robotic manipulators to handle heavy-duty construction tasks. These robots are capable of lifting and moving significant loads.
The University of Houston also plays a vital role. The C.R.A.F.T. Lab at the university actively trains new talent and tests advanced technologies. For instance, C.R.A.F.T. engineers use LIDAR-equipped drones to quickly and accurately scan construction sites, helping to create detailed 3D models.
Houston boasts a significant advantage. Ranked by Built In as a top ten city for robotics firms in the U.S., these companies view each other as collaborators, not rivals. This creates a powerful local ecosystem, ensuring that local construction contractors get access to cutting-edge solutions without needing to bear global investment costs.
Technology in Action
Imagine an autonomous rover crawling across freshly poured concrete, printing the outlines of columns and pipe runs with millimeter precision. Rugged Robotics deployed such a platform on a Brogoitti Construction project, where the team cut the installation timeline from eight weeks down to two. They effectively saved 75% of the time. Another case in point: the Mesquite Government Center by Suffolk Construction, where automation reduced rework by 75% and layout time by 60%. These figures, documented in AGC Houston industry reports, illustrate how machines eliminate human error, freeing up skilled workers to concentrate on more complex tasks. University tests with photogrammetry add another layer, with drones mapping terrain to minimize risks on uneven surfaces.
The Hidden Perks of Automation
Automation in Houston is about far more than just construction speed. It fundamentally boosts site safety. According to OSHA data, the construction industry accounts for about 20% of injuries from falls. Robots take over these dangerous and monotonous operations, removing the human element where the risk is highest.
Resource efficiency is equally impressive. Algorithms optimize material use, leading to a significant reduction in construction waste. Companies like Rugged Robotics confirm that their fleet of devices operates 24/7 without breaks, regardless of the oppressive heat or sudden downpours typical of Texas.
These changes have an important environmental dimension. Fewer on-site errors mean fewer truck trips for delivering extra materials or hauling away debris. This, in turn, cuts down on emissions. For construction contractors, this translates into increased competitiveness: their projects now finish on time and their budgets reliably stay within the set limits. Robots are making construction smarter and safer.
Overcoming Hurdles and the Future Vision
However, the adoption of robotics in Houston faces challenges. Not everything goes smoothly. Initial investment in new equipment is substantial, potentially reaching tens of thousands of dollars, which constrains small construction firms. Furthermore, staff training takes time, as workers must master complex BIM modeling software. A Clutch.co survey indicates that a third of Houston companies cite a shortage of qualified technicians. There are also regulatory hurdles: OSHA standards are slow to update, and integrating new methods often meets resistance from industry veterans. Yet, pilot programs like those run by Rugged demonstrate rapid returns. Investments are recouped within 6–12 months, quickly turning skeptics into innovation advocates.
Despite the difficulties, the industry’s horizons are continually expanding. By 2030, McKinsey predicts automation will cover nearly half of construction tasks. In Houston, this means forming hybrid teams: people will handle strategic planning while machines take on execution. Rugged plans to expand its fleet to operate on solar farms. Meanwhile, university labs are focused on 3D-printed elements made from recycled materials. The growth of the energy market also drives development; for example, Helix Energy is creating robots for inspecting underwater oil rigs. The city has every chance of becoming a global hub, exporting construction know-how to Latin America, a region undergoing rapid urbanization. The Houston experience is set to define the future of building across the entire region.
A New Era for the City
Houston is proving how technology can turn chaos into a symphony. From its NASA roots to its concrete foundations, automation promises sustainable growth. An industry that once struggled with shortages is now thriving on innovation. The next time you drive past a crane, take a closer look: a rover might be hiding there, drawing the future.
